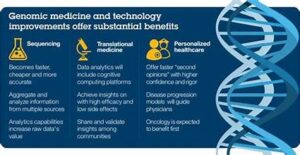
The healthcare industry is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by advanced genomic technologies. These innovations promise to revolutionize how we understand, diagnose, and treat diseases, offering unprecedented opportunities for personalized medicine and improved patient outcomes. This article explores the impact of genomic technologies on healthcare, highlighting their potential to reshape the industry.
1. Understanding Genomic Technologies
Genomic technologies involve the study of genes and their functions. They include techniques for sequencing DNA, analyzing genetic variations, and understanding gene expression. Key technologies in this field include:
- Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS): This technology allows for rapid sequencing of entire genomes or targeted regions, providing comprehensive genetic information.
- CRISPR-Cas9: A groundbreaking tool for gene editing that enables precise modifications to DNA, offering potential treatments for genetic disorders.
- Genomic Databases: Large-scale repositories of genetic information that facilitate research and the development of new therapies.
2. Personalized Medicine
One of the most significant impacts of genomic technologies is the advancement of personalized medicine. Unlike traditional treatments that are often one-size-fits-all, personalized medicine tailors therapies to the individual characteristics of each patient. This approach is made possible by:
- Genetic Profiling: By analyzing a patient’s genetic makeup, healthcare providers can identify predispositions to certain diseases and select the most effective treatments.
- Pharmacogenomics: This field studies how genes affect a person’s response to drugs, allowing for customized medication plans that minimize adverse effects and maximize efficacy.
- Predictive Analytics: Genomic data can predict the likelihood of developing certain conditions, enabling early intervention and preventive measures.
3. Advancements in Disease Diagnosis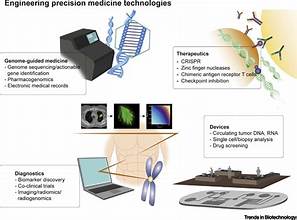
Genomic technologies have dramatically improved disease diagnosis by:
- Early Detection: Advanced sequencing techniques can identify genetic mutations associated with diseases at an early stage, leading to earlier and more accurate diagnoses.
- Rare Diseases: Many rare diseases have a genetic basis. Genomic sequencing helps in identifying the specific genetic mutations responsible, facilitating diagnosis and management.
- Cancer Detection: Genomic profiling of tumors can reveal specific mutations driving cancer growth, allowing for targeted therapies that address the underlying genetic causes.
4. Gene Therapy and Editing
Gene therapy and editing represent cutting-edge applications of genomic technologies with the potential to cure genetic disorders. These methods include:
- Gene Replacement Therapy: Introducing a healthy copy of a gene to compensate for a defective one, potentially curing inherited diseases.
- Gene Editing: Techniques like CRISPR-Cas9 can correct genetic mutations at precise locations, offering the possibility of treating or even curing genetic disorders such as cystic fibrosis and muscular dystrophy.
- Somatic Cell Gene Therapy: Editing the genes in specific cells of a patient to treat diseases without affecting the patient’s germline (reproductive cells).
5. Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite the promising advancements, the use of genomic technologies in healthcare raises several challenges and ethical considerations:
- Data Privacy: Handling and protecting sensitive genetic information is crucial. Ensuring that genetic data is stored securely and used responsibly is a major concern.
- Equity and Access: There is a risk that advanced genomic technologies may exacerbate existing health disparities if access is limited to certain populations or regions.
- Ethical Implications: The ability to edit genes raises ethical questions about the potential for unintended consequences, including long-term impacts on future generations.
6. Future Directions
The future of genomic technologies in healthcare is bright, with ongoing research and development paving the way for even more transformative applications. Key areas of focus include:
- Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI): Combining genomic data with AI algorithms can enhance the accuracy of disease predictions and treatment recommendations.
- Expansion of Genomic Databases: Increasing the diversity of genomic data available will improve the understanding of genetic variations across different populations.
- Advancements in Gene Editing: Continued refinement of gene editing techniques will likely lead to safer and more effective therapies.
Conclusion
Advanced genomic technologies are revolutionizing healthcare by enabling personalized medicine, improving disease diagnosis, and offering new therapeutic possibilities. While challenges and ethical considerations remain, the ongoing advancements in this field hold the promise of a future where healthcare is more precise, effective, and equitable. Embracing these technologies and addressing their challenges will be crucial in realizing their full potential and transforming healthcare for the better.



